One of the Most Common Inherited Diseases
Cystic fibrosis is one of the most common inherited diseases in the western world, with an incidence of 1:2500 births. It is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner and frequency of the carriers is estimated at 1:20 to 1:25 people.
It is a serious condition that affects many organs, such as the respiratory, digestive and pancreatic. In men, some mutations can cause infertility (bilateral lack of vas deferens [CBAVD]).
Cystic Fibrosis Mutations
The gene which is responsible for Cystic Fibrosis was identified in 1989 and is called cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR). Today, they have been detected more than 1600 defects (mutations) in the genetic material of patients with cystic fibrosis. The majority of them are considered pathological, while frequency is depending on geographic and demographic factors.
DF508 is the most common gene mutation in Greece with a frequency of 53.4% and is considered the heaviest in symptomatology mutations.
The next most frequent mutations in Greece, covering 71.1% of the Greek population, are:
- 621+1G>T (5,7%)
- G542X (3,9%)
- N1303K (2,6%)
- 2789+5G>A (1,7%)
- 2183AA>G (1,4%)
- E822X (1,4%)
- R1158X (1%)
The rest have incidence less than 1%.
Cystic Fibrosis & Fertilization
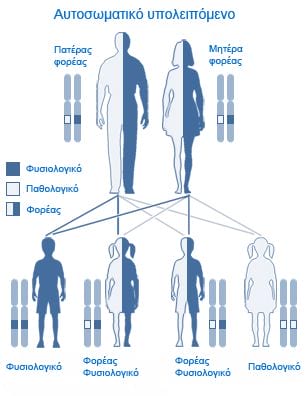
Each individual carries two copies of the CFTR gene. For someone to suffer from cystic fibrosis they should carry mutations in both copies of the gene, that is to be homozygous. If someone carries a mutation in only one copy, i.e. heterozygote, is called a carrier of the disease.
To prevent a child to be born with cystic fibrosis, both parents should not carry mutations or at least only one of the two. If both parents are carriers, then there is a 25% chance for a child to be born with cystic fibrosis.
Testing of Cystic Fibrosis
The only way to recognize the carriers of cystic fibrosis is by molecular genetic testing that detects mutations in the CFTR gene in the general population. Screening for cystic fibrosis to identify carriers of the disease is performed:
- during family planning
- when there is family history
- when there is echogenic bowel on ultrasound
- in cases of infertility
In case of family planning, if both parents are carriers, information about the fetus is given by methods of preimplantation diagnosis and prenatal screening.
